
For example, if XYZ company expected to produce 400 widgets in a period but ended up producing 500 widgets, the cost of materials would be higher due to the total quantity (volume) produced. This type of standard costing believes the perfect condition when there is no interruption and wastage during production. They believe that there is no machine breakdown, worker tea break, or any error in the production process.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
The total cost per unit of standard and custom product can be calculated by adding up – direct cost, raw material cost, and ABC derived per unit indirect cost. Standard cost accounting can hurt managers, workers, and firms in several ways. For example, a policy decision to increase independent contractor invoice template inventory can harm a manufacturing manager’s performance evaluation. Increasing inventory requires increased production, which means that processes must operate at higher rates. When something goes wrong, the process takes longer and uses more than the standard labor time.
- For this reason, historical costing is simply a post-mortem of a case and has its own limitations.
- If it determines the actual costs are lower than expected, the variance is favorable.
- These standards are used only when they are likely to remain constant or unaltered over a long period.
- These symptoms related to confusion about prices in themarketplace versus product cost, use of volume-related bases to allocateoverhead, and high inventory values.
Calculating Standard Costs
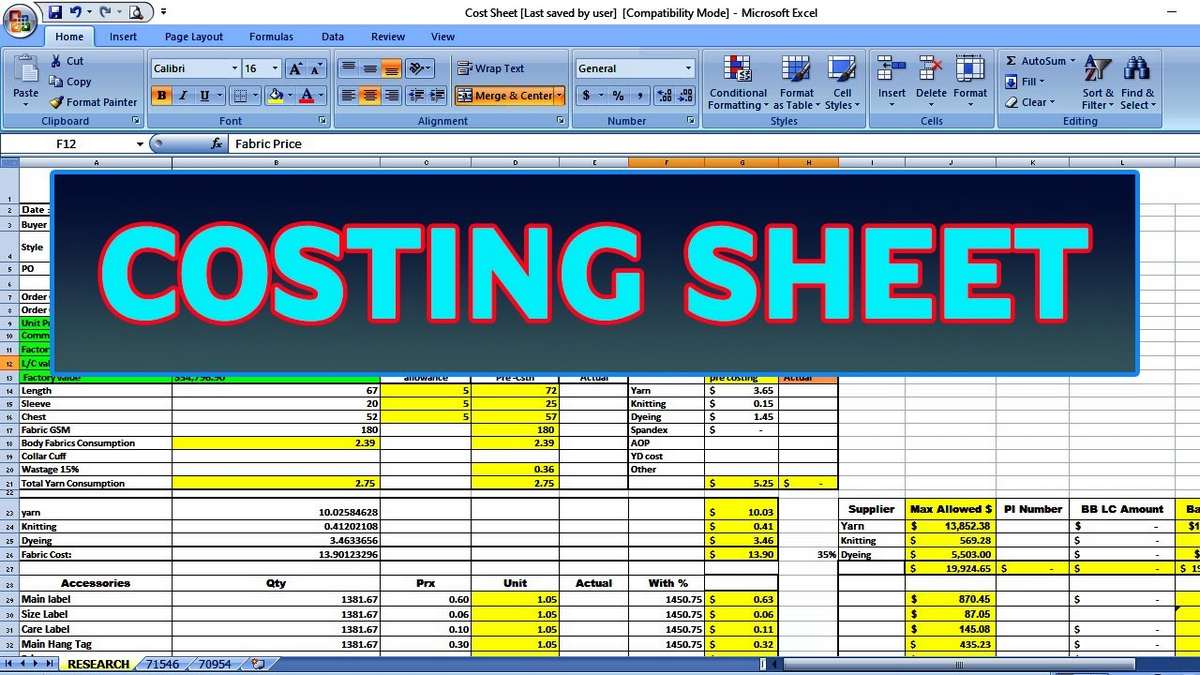
These standard costs could be based on historical data, past experiences, market averages, and other relevant bases. When using lean accounting, traditional costing methods are replaced by value-based pricing and lean-focused performance measurements. Financial decision-making is based on the impact on the company’s total value stream profitability. Value streams are the profit centers of a company; a profit center is any branch or division that directly adds to a company’s bottom-line profitability. For example, suppose there is a company that produces both trinkets and widgets.
Standard Costs
Uncontrollable variances, on the other hand, stem from external factors like market price fluctuations or changes in regulatory requirements. By distinguishing between these types of variances, companies can focus their efforts on areas where they can make a tangible impact, while also preparing for external challenges that may affect their cost structure. Standard labor costs are calculated by considering the time required to complete a task and the wage rate of the employees involved.
The fundamental for decision on allocation of overheads is the output of a process in each hour. Standard cost involves different elements of costs, such as material, labor and overheads, in respect of a product. Difficulties for Small Industries’ establishment of standards and their implementation involve initial high costs.
The contractordid comment that the government brought its legal and financial teams aswell as DCAA to review the proposal. Variances arise are disposed off by transferring it the relevant accounts (costing profit and loss account) as per the accounting method (plan) adopted. Standard costing is expensive and unsuitable for job manufacturing industries as they manufacture non standardized products such as catering, tailoring, printing, etc. Standard Costing is defined as the use of Standard Costs in measuring and controlling the performance of a company. In layman’s terms, it means comparing your actual cost with what you have budgeted.
Finding differences (variances) between actual costs and standard costs. The difference between actual costs and standard costs is known as “variance”. There is a favorable variance when actual costs are less than standard costs. An unfavorable variance occurs when actual costs are higher than the standard.
In contrast to general accounting or financial accounting, cost accounting is an internally focused, firm-specific method used to implement cost controls. Cost accounting can be much more flexible and specific, particularly when it comes to the subdivision of costs and inventory valuation. Cost-accounting methods and techniques will vary from firm to firm and can become quite complex. In summary, understanding actual costs allows FP&A teams to provide more accurate, insightful financial analysis that supports better decision-making, budgeting, and long-term strategic planning.

